Hello! Welcome to Nanjing Runtime environmental protection technology Co., LTD
Hello! Welcome to Nanjing Runtime environmental protection technology Co., LTD




Chemical name: Trimesic acid/pyromellitic acid
Chinese name: 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid
English name: Benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylic acid,
TMA, H3BTC, BTC
CAS No.:209-077-7
EINECS login number: 209 077 7
Molecular formula:C9H6O6
Molecular weight:?210.14
Structural formula:
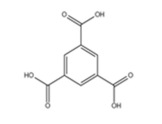
Trimesic acid, also known as 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid, has a self-organized 2D molecular network
structure, which is formed by intermolecular hydrogen bonds between carboxylic acid residues in block
crystals. Character: White crystalline powder. Standard Heat of combustion (enthalpy) of crystalline
phase (kJ · mol-1): -3208.96, standard heat of formation of crystalline phase (enthalpy)(
KJ · mol-1): -1190.14, melting point (o C): 380, flash point: 328 ℃
Solubility: Easily soluble in ethanol, soluble in ether, and soluble in 40 parts of water at 23
℃.
| Indicator Name | Unit | Content |
| Loss on drying | [%] | ≤0.5 |
| Acid value | mgKOH/g | 780-800 |
| Total chlorine | ppm | ≤ 50ppm |
| Content(HPLC) | % | ≥99 |
| Clarity | —— | Clear and transparent, without mechanical impurities |
Trimesic acid, namely 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid, is a new important chemical raw material with
high added value. Trimesic acid molecule has three symmetrical carboxyl functional groups, which is an
important fine chemical intermediate, and can be used to produce and synthesize downstream products with
various uses. For example, benzoyl chloride is used to prepare reverse osmosis membrane materials for
seawater desalination; Tri Allyl group phenyl homotriate is used as curing and crosslinking agent of
unsaturated polyester resin; High performance plasticizer; Alkyd resin type water-soluble baking paint
and melamine resin modified paint, etc. In addition, it can also coordinate with rare earth metal ions
to form fluorescent ligands for the separation and purification of rare earth ions. And used as raw
materials for the production of ultra-low temperature adhesives, anticancer drugs, plant growth
regulators, fungicides, and preservatives.
In recent years, in the research of Metal–organic framework (MOFs) and Covalent organic framework
(COFs), Trimesic acid has been used to synthesize pyromellitic acid based organic framework materials,
which is an excellent organic ligand. MOFs materials are a new type of porous material that emerged at
the beginning of this century, composed of metal and organic ligands. The metal part is usually called a
metal node, which is composed of metal and oxygen atoms, hydroxyl groups, carboxylic acids, etc; The
organic ligand part is mostly polycarboxylic acid (such as Trimesic acid). The most researched areas
include gas adsorption and separation, chemical induction, heterogeneous catalysis, and drug delivery.
The internal pores of MOFs are like small gas storage tanks, which can store a large number of gas
molecules and have good effects on the storage and separation of oxygen, methane, and carbon monoxide.
At present, the synthetic routes of Trimesic acid acid mainly include Mesitylene nitric acid oxidation,
Mesitylene Potassium permanganate oxidation and Mesitylene liquid phase air oxidation. Mesitylene is
used as the raw material for the three methods.
Among them, the liquid-phase air oxidation method uses compressed air as raw material to oxidize
Mesitylene, which requires adding catalyst and initiator. Compared with the previous two methods, the
third method has high selectivity and yield, low raw material cost, and is currently considered a more
efficient and advanced method.
1. Nitric acid oxidation of Mesitylene
As early as 1948, Lawton et al. proposed the method of synthesizing Trimesic acid by oxidizing alkyl
aromatics with nitric acid at 220 ℃ and 3.5 MPa. The method uses Mesitylene as raw material, nitric acid
with concentration of 20% as oxidant, and reacts under medium and high pressure to produce Trimesic acid
acid.
Disadvantages: The use of nitric acid as a raw material has high costs, poor selectivity for the target
product, high difficulty in refining the product, serious environmental pollution, and high risk of
explosion.
2. Mesitylene Potassium permanganate oxidation method
On the basis of nitric acid oxidation method, the contact medium area between the inorganic phase
Potassium permanganate solution and the organic phase Mesitylene is increased by introducing catalysts
such as hexadecyl Trimethylamine bromide, octadecyl amine dimethyl hydroxynitrate Quaternary ammonium
cation, etc., thus improving the reaction rate and product yield of the process.
Disadvantages: There are also high costs, low yields, and serious environmental pollution issues. The
consumption of Potassium permanganate is 10 times of that of raw materials. The production cost is high,
and the production process is also dangerous. A large amount of wastewater and waste residue are
generated, which is difficult to be treated after treatment and easy to pollute the environment. In
addition, the purity of the reaction product is low, and the purification process is relatively complex.
3. Liquid phase air oxidation of Mesitylene
This method is prepared by feeding oxygen into the catalytic system composed of cobalt salt and bromide,
that is, liquid Mesitylene is oxidized to Trimesic acid with air at 2-3MPa and 200-230 ℃ using cobalt
salt as catalyst.
Disadvantages: Traditional catalysts have low catalytic efficiency, low conversion and selectivity.
Compared with other oxidation methods, the advantage of liquid phase air oxidation method lies in the
use of inexpensive and easily available compressed air as an oxidant, thereby reducing the cost of raw
materials; In addition, this method improves the product yield.



Yellow crystalline powder, odorless, can sublimate. Slightly soluble in water......


RT-101 1, 3-bis (4, 5-dihydro2-oxazole) benzene (dioxazoline) is an important organic......


RT-52 CAS :6334-25-4 is a crosslinking curing agent for thermoplastic solid powder coatings......